[Algorithm] 6장 자료구조 - 해쉬 테이블(Hash Table)

해쉬 테이블
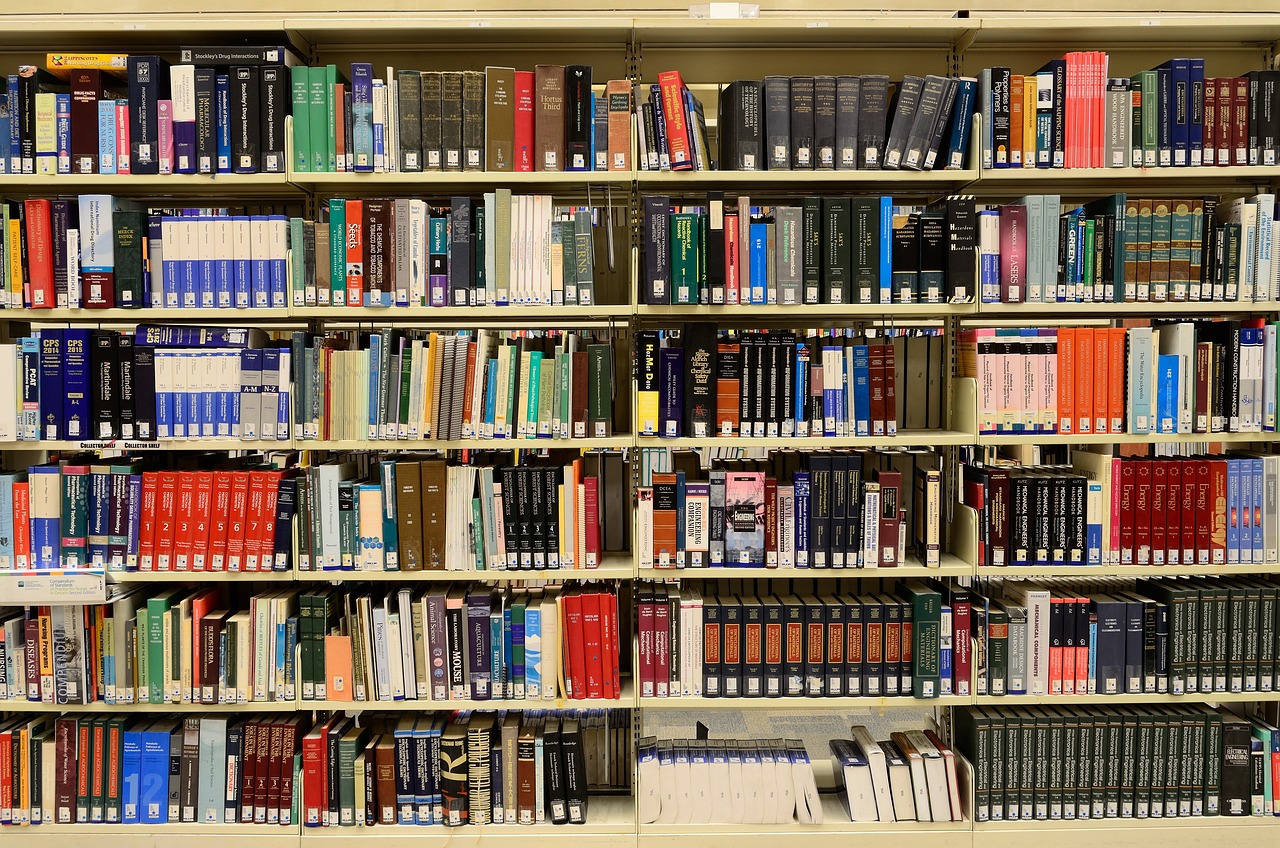
해쉬 테이블은 (Key, Value)로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조 중 하나로 빠르게 데이터를 검색할 수 있는 자료구조이다.
해쉬 테이블이 빠른 검색속도를 제공하는 이유는 내부적으로 배열(버킷)을 사용하여 데이터를 저장하기 때문이다.
해쉬 테이블은 각각의 Key값에 해시함수를 적용해 배열의 고유한 index를 생성하고, 이 index를 활용해 값을 저장하거나 검색하게 된다. 여기서 실제 값이 저장되는 장소를 버킷 또는 슬롯이라고 한다.
- 해쉬 함수(Hash Function) - 임의의 데이터를 고정된 길이의 값으로 리턴해주는 함수
- 해쉬 (Hash), 해쉬 값(Hash Value), 또는 해쉬 주소(Hash Address) - 해싱 함수를 통해 리턴된 고정된 길이의 값
- 해쉬 테이블(Hash Table) - 키 값의 연산에 의해 직접 접근이 가능한 데이터 구조
- 슬롯(Slot) - 해쉬 테이블에서 한 개의 데이터를 저장할 수 있는 공간
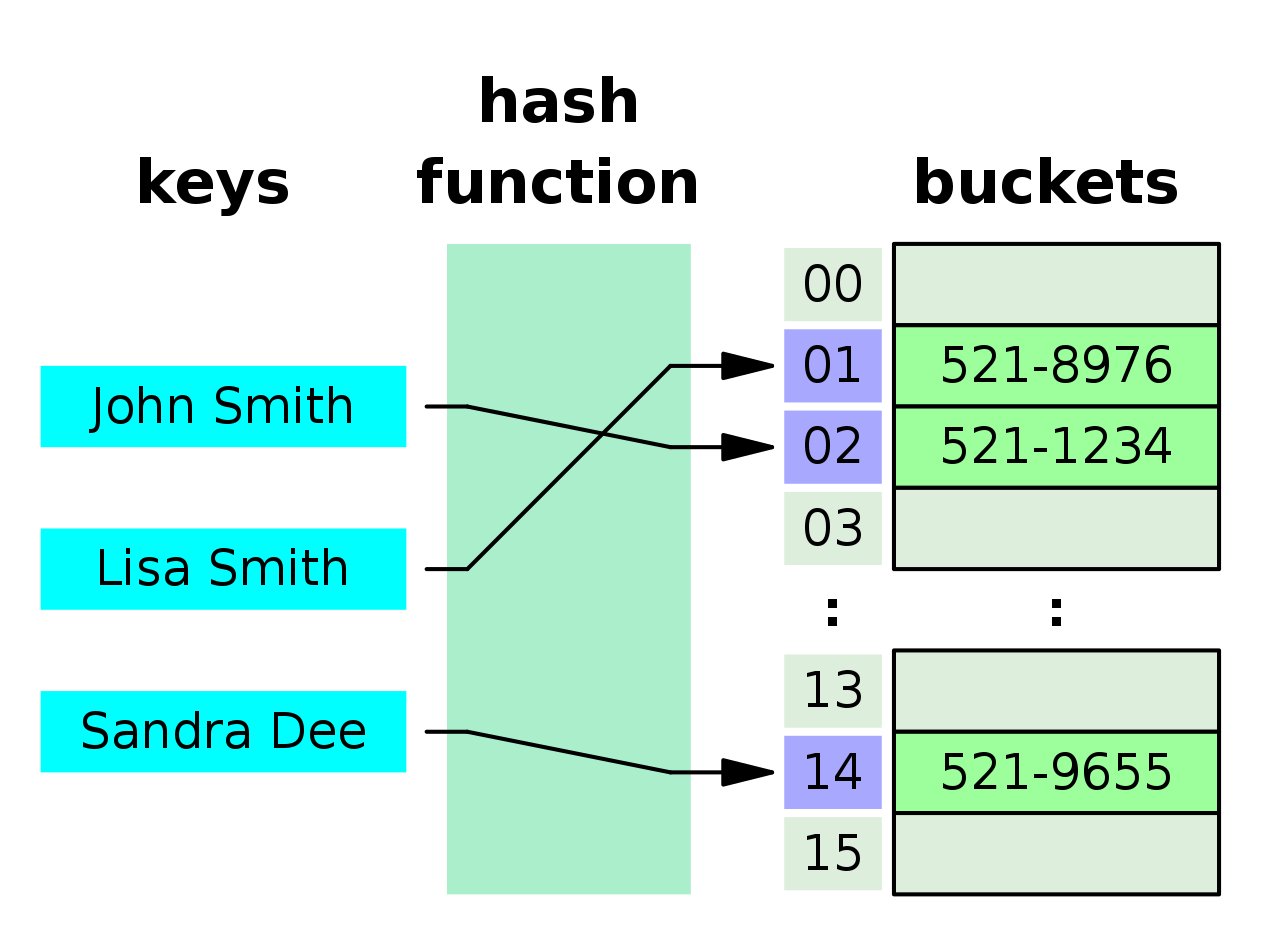
- 장점
- 데이터 저장,검색 속도가 빠르다. - 키를 통해 해당 데이터에 바로 접근이 가능하다.
- 단점
- 메모리가 좀더 많이 필요하다.
- 여러 키에 해당하는 주소가 동일할 경우 충돌을 해결하기 위한 별도의 자료구조를 추가해야 한다.
- 주요 용도
- 검색이 많이 필요할 경우
- 저장,삭제,읽기가 빈번한 경우
- 캐쉬 구현 - 중복 확인이 쉽다.
간단한 해쉬
간단한 해쉬를 만들어 보자
public class MyHash {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size){
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot{
String value;
Slot(String value){
this.value = value;
}
}
}
해쉬 함수
해쉬 함수에서 중요한 것은 고유한 인덱스 값을 설정하는 것이다. 해쉬 테이블에 사용되는 대표적인 해쉬 함수로는 아래의 4가지가 있다.
- Division Method: 나눗셈을 이용하는 방법으로 입력값을 테이블의 크기로 나누어 계산한다.( 주소 = 입력값 % 테이블의 크기) 테이블의 크기를 소수로 정하고 2의 제곱수와 먼 값을 사용해야 효과가 좋다고 알려져 있다.
- Digit Folding: 각 Key의 문자열을 ASCII 코드로 바꾸고 값을 합한 데이터를 테이블 내의 주소로 사용하는 방법이다.
- Multiplication Method: 숫자로 된 Key값 K와 0과 1사이의 실수 A, 보통 2의 제곱수인 m을 사용하여 다음과 같은 계산을 해준다. h(k)=(kAmod1) × m
- Univeral Hashing: 다수의 해시함수를 만들어 집합 H에 넣어두고, 무작위로 해시함수를 선택해 해시값을 만드는 기법이다.
간단하게 1번의 방법으로 해쉬 함수를 만들자.
public class MyHash {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size){
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot{
String value;
Slot(String value){
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunc(String key){
return (int)key.charAt(0) % this.hashTable.length;
}
}
데이터 저장 메소드 추가
- 객체 배열 선언시, 각 배열의 아이템은 각 객체를 참조할 수 있는 주소를 담을 수 있는 공간만 할당한다.
- 각 아이템 생성시, 별도로 각 객체를 생성
- 객체 배열 선언시, 각 생성할 객체를 가리킬 주소만 저장할 공간을 배열로 만드는 것
public class MyHash {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size){
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot{
String value;
Slot(String value){
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunc(String key){
return (int)key.charAt(0) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean saveData(String key, String value){
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null){
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
}else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(value);
}
return true;
}
}
해쉬 함수로 고유 주소값을 만든뒤 해당 위치에 데이터를 넣으면 된다.
데이터 가져오는 메소드 추가
키를 입력하면 해당 키를 해쉬함수로 주소로만들어 해당 주소에 데이터가 있는지 확인한다.
public class MyHash {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHash(Integer size){
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot{
String value;
Slot(String value){
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunc(String key){
return (int)key.charAt(0) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean saveData(String key, String value){
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null){
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
}else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(value);
}
return true;
}
public String getData(String key){
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null){
return this.hashTable[address].value;
}else {
return null;
}
}
}
결과
MyHash mainObject = new MyHash(20);
mainObject.saveData("Kim", "01011112222");
mainObject.saveData("Lee", "01033334444");
mainObject.getData("Kim");
//결과 : 01011112222
주소 충돌 해결
만약 “Kimgugu”를 해시 함수를 돌려 나온 값과 “Kimdudu”를 해시 함수를 돌려 나온 값이 동일하다면 어떻게 해야 할까?
해시 테이블에서는 충돌에 의한 문제를 분리 연결법(Separate Chaining)과 개방 주소법(Open Addressing) 크게 2가지로 해결하고 있다.
Chaining 사용 해쉬
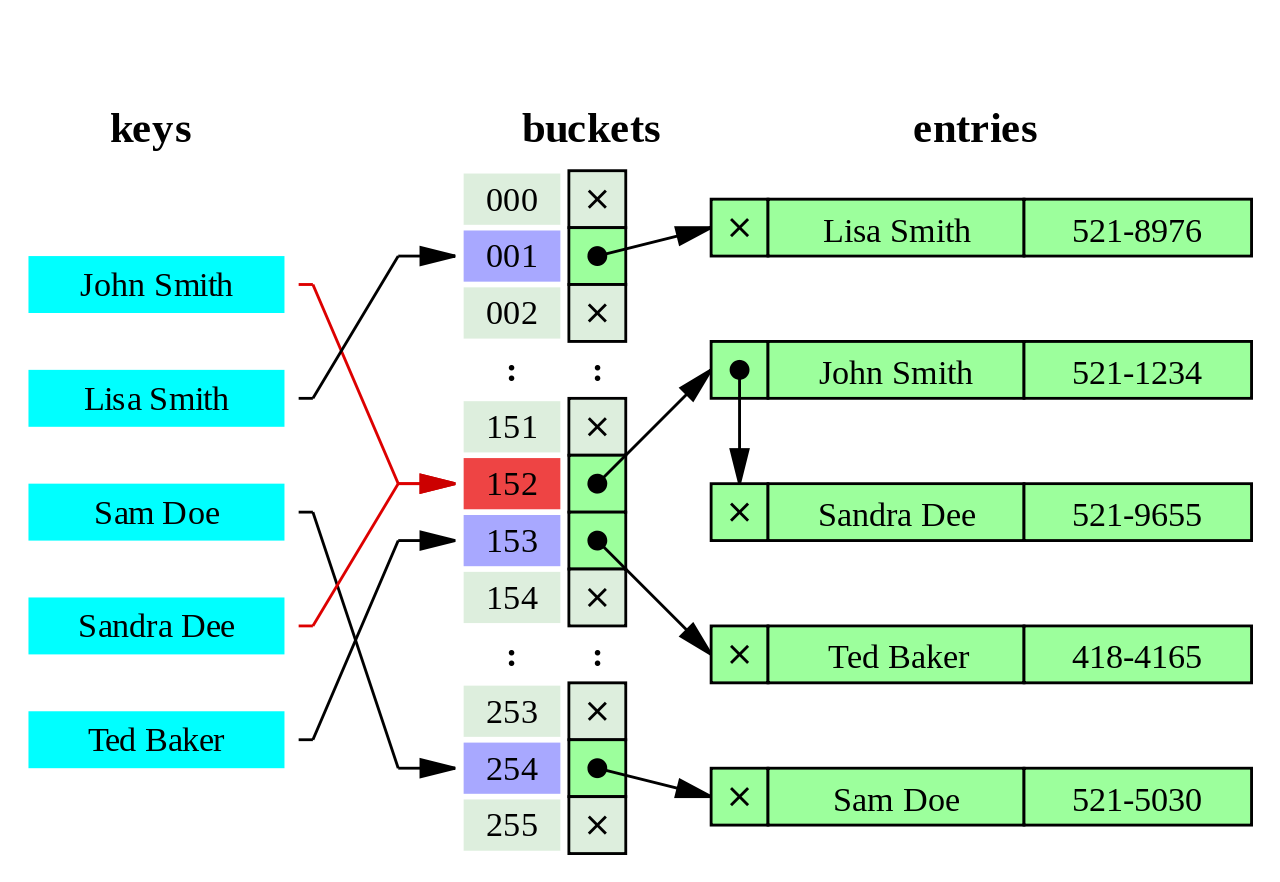
동일한 버킷의 데이터에 대해 자료구조를 활용해 추가 메모리를 사용하여 다음 데이터의 주소를 저장하는 것이다. 위의 그림과 같이 동일한 버킷으로 접근을 한다면 링크드 리스트 형식으로 데이터들을 연결을 해서 관리한다.
public class MyHashChaining {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHashChaining(Integer size){
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot{
String key;
Slot next;
String value;
Slot(String key, String value){
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunc(String key){
return (int)key.charAt(0) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean saveData(String key, String value){
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null){
Slot findSlot = this.hashTable[address];
Slot prevSlot = this.hashTable[address];
while (findSlot != null){
if (findSlot.key == key){
findSlot.value = value;
return true;
}else {
prevSlot = findSlot;
findSlot = findSlot.next;
}
}
prevSlot.next = new Slot(key, value);
}else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(key, value);
}
return true;
}
public String getData(String key){
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address]!= null){
Slot findSlot = this.hashTable[address];
while (findSlot != null){
if (findSlot.key == key){
return findSlot.value;
}else {
findSlot = findSlot.next;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
Slot클래스를 수정한다. 링크드 리스트처럼 다음 데이터로 넘어가야하기때문에 키값과 next변수를 가진다.
데이터 저장
해당 주소가 비어있으면 그저 그 주소에 새 객체를만들어 데이터를 저장하면된다.
하지만 해당 주소에 데이터가있으면 그 주소의 링크드리스트 데이터의 끝에 데이터를 저장한다.
데이터 검색
먼저 검색할 키로 주소를 확인한뒤 키 값이 동일한지 확인한다. 만약 주소는 같고 키가 다르면 다음 데이터를 가져와 비교한다.
Linear Probing 사용 해쉬
현재의 버킷 index로부터 고정폭 만큼씩 이동하여 차례대로 검색해 비어 있는 버킷에 데이터를 저장한다.
해쉬 테이블 저장공간 안에서 충돌 문제를 해결하는 기법이다.
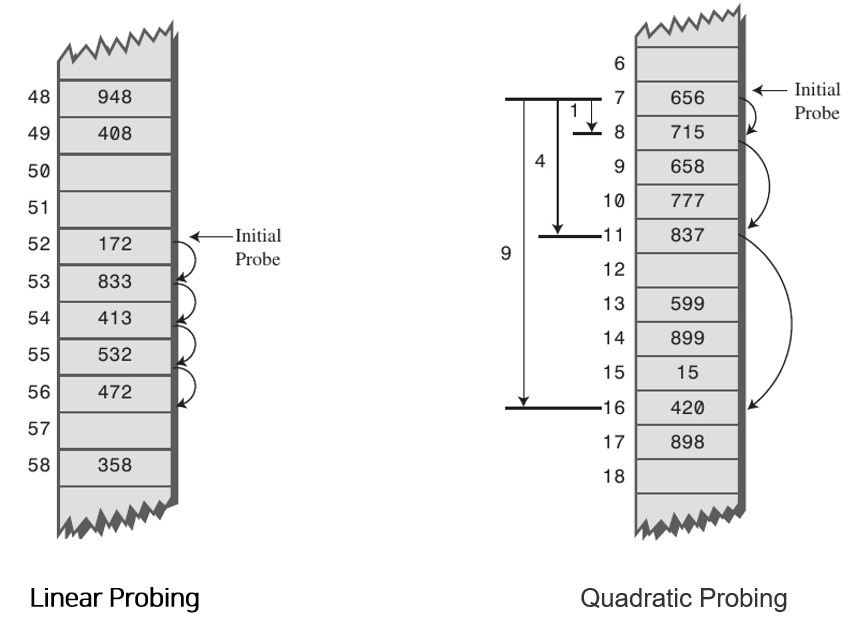
public class MyHashLinearProbing {
public Slot[] hashTable;
public MyHashLinearProbing(Integer size){
this.hashTable = new Slot[size];
}
public class Slot{
String key;
String value;
Slot(String key, String value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public int hashFunc(String key){
return (int)key.charAt(0) % this.hashTable.length;
}
public boolean saveData(String key, String value){
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address]!= null){
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key){
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
}else {
Integer currAddress = address + 1;
while (this.hashTable[currAddress] != null){
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key){
this.hashTable[address].value = value;
return true;
}else {
currAddress ++;
if (currAddress >= this.hashTable.length){
return false;
}
}
}
this.hashTable[currAddress] = new Slot(key,value);
return true;
}
}else {
this.hashTable[address] = new Slot(key, value);
}
return true;
}
public String getData(String key){
Integer address = this.hashFunc(key);
if (this.hashTable[address] != null){
if (this.hashTable[address].key == key){
return this.hashTable[address].value;
}else {
Integer currAddress = address + 1;
while (this.hashTable[address] != null){
if (this.hashTable[currAddress].key == key){
return this.hashTable[currAddress].value;
}else {
currAddress ++;
if (currAddress >= this.hashTable.length){
return null;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}else {
return null;
}
}
}
데이터 저장
해당 주소에 데이터가 이미 들어있으면 다음 주소에 데이터를 추가한다. 만약 주소를 계속 이동하다 버킷의 끝에 다다르면 저장은 실패한다.
만약 버킷이 전부 차게되면 더큰 크기로 새로 생성해야한다.
데이터 검색
키를 통해 해당 주소로갔을때 키값이 서로 다르면 저장 할때와 마찬가지로 다음 주소로 이동한다. 이동하다 버킷의 끝에 다다르면 검색을 중지한다.
빈번한 충돌 개선 방법
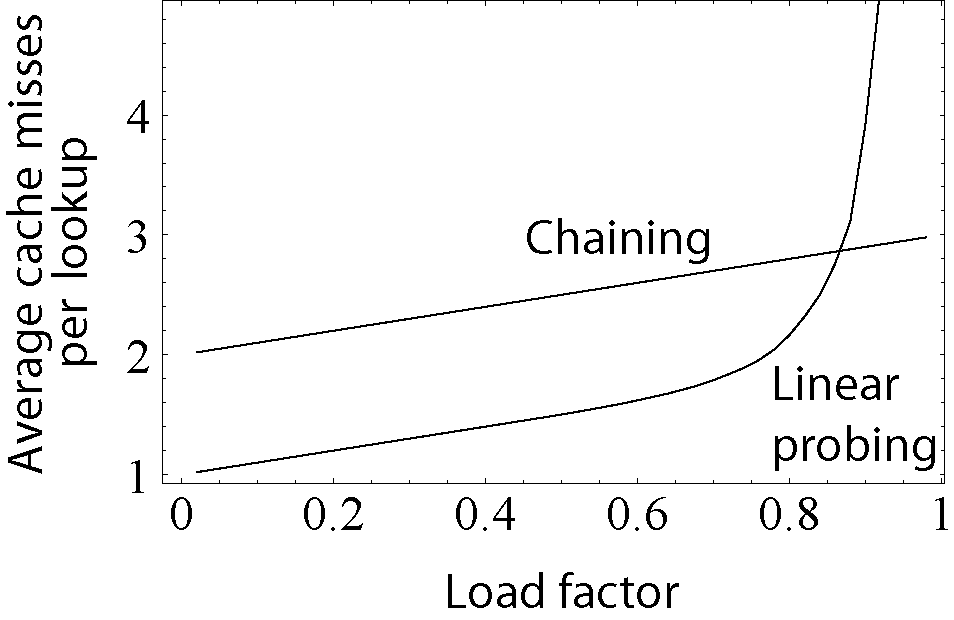
충돌이 일어났을 경우 걸리는 부하를 그래프로 표현한것이다.
선형 프로빙은 버킷내부에서 처리하기때문에 일정 수준 이하에서는 더 잘 수행되지만 테이블이 가득차면 급격하게 성능이 하락한다.
충돌을 한다는건 값들의 경우의 수가 적다는 것을 의미한다.
해쉬 테이블의 저장공간을 늘리거나 해쉬 함수를 좀더 여러 값이 나올 수 있도록 재정의한다.
String name = "Dave";
int key = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) {
key += name.charAt(i);
}
(int)(key) % 200
시간 복잡도
각각의 Key값은 해시함수에 의해 고유한 index를 가지게 되어 바로 접근할 수 있으므로 평균 O(1)의 시간복잡도로 데이터를 조회할 수 있다.
하지만 데이터의 충돌이 발생한 경우 Chaining에 연결된 리스트들까지 검색을 해야 하므로 O(N)까지 시간복잡도가 증가할 수 있다.
(통계적으로 해시 테이블의 공간 사용률이 70% ~ 80%정도가 되면 해시의 충돌이 빈번하게 발생하여 성능이 저하되기 시작한다고 한다.)
- 일반적인 경우(Collision이 없는 경우)는 O(1)
- 최악의 경우(Collision이 모두 발생하는 경우)는 O(n)
해쉬 테이블의 경우는 일반적인 경우를 기대하고 작성한다.
Java에서 HashMap과 HashTable차이
Java에서 HashTable과 HashMap의 차이는 여러가지 있겠지만 가장 큰 차이는동기화 지원 여부에 있다.
// 해시테이블의 put
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 해시맵의 put
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
위의 코드에서 첫번째 put은 해시테이블의 put이며, 두번째 put은 해시맵의 put이다.
첫번째 해시테이블의 put에는 synchronized가 걸려있기 때문에 멀티 스레드 환경에서 데이터 조작에 대한 일관성이 보장된다.
