[Algorithm] 5장 자료구조 - 링크드 리스트(Linked List)

링크드 리스트(Linked List)
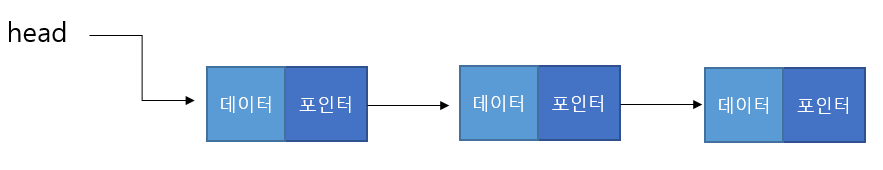
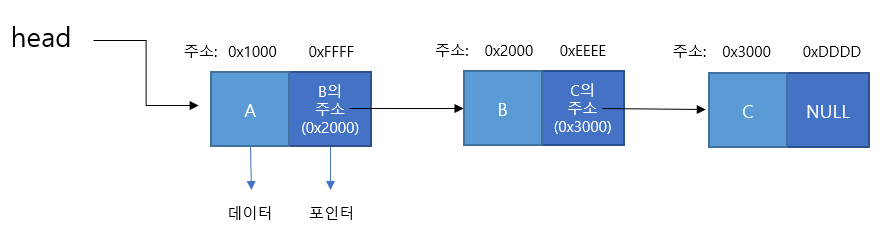
각 노드가 데이터와 포인터를 가지고 한 줄로 연결되어 있는 방식으로 데이터를 저장하는 자료구조이다.
- 노드(Node): 데이터 저장 단위 (데이터값, 포인터) 로 구성
- 첫번쩨 노드를 헤드(head) 마지막 노드를 테일(tail)이라고 한다.
- 포인터(pointer): 각 노드 안에서, 다음이나 이전의 노드와의 연결 정보를 가지고 있는 공간
장점
- 삽입과 삭제가 용이 - 포인터로 연결되어 있어 가리키는 노드만 변경해주면 된다.
- 가변적 크기 - 새로운 데이터 추가시 동적으로 크기가 변경된다.
- 불연속 메모리 할당 - 빈 공간 없이 데이터를 저장할 수 있다., 사용한 메모리를 재사용 할 수 있다.
단점
- 인덱스 접근이 불가능 - 반복자를 이용하여 탐색하기 때문에 속도가 느리다.
- 포인터로 인한 저장 공간 낭비 - 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터를 저장하는 공간이 필요하다.
사용처
- 크기가 정해져 있지 않을때
- 삽입과 삭제가 자주 일어날 때
- 검색을 자주 하지 않을 때
간단한 링크드 리스트
자바로 리스트를 구현해본다.
public class Node<T> {
T data; //노드에 저장될 데이터
Node<T> next = null; //다음 노드를 가르키는 인스턴스
//생성자
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
각각의 노드를 생성하고 연결하면 링크드 리스트가 된다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node<String> node1 = new Node("a");
Node<String> node2 = new Node("b");
node1.next = node2;
Node<String> head = node1; //노드의 가장앞을 헤드라 부른다.
System.out.println(node1.data);
System.out.println(node1.next.data);
}
싱글 링크드 리스트
포인트가 다음 노드만 바라보고있는걸 싱글 링크드라고한다. 여러가지 기능을 추가해보자.
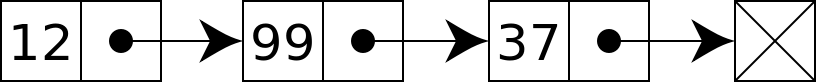
노드 추가
노드 추가는 리스트가 비어있을때와 비저 있지 않았을때, 두가지로 나눌 수 있다.
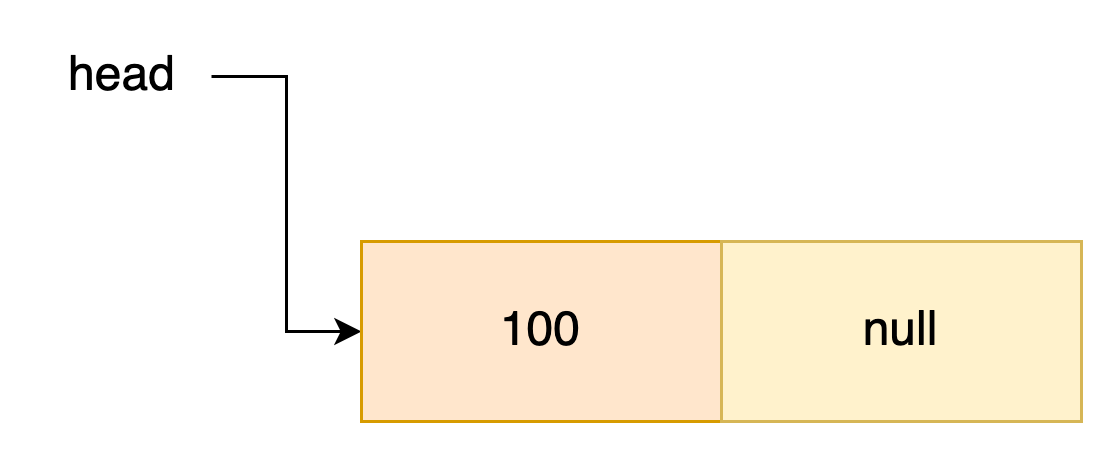
- 리스트가 비어 있을 경우
첫번째 노드로 정수 100을 데이터로 갖는 노드를 추가한다고하자, 간단하게 newNode를 만든 후 head가 newNode로 되도록 한다. 리스트가 비어있는것은 head == null 인것을 확인하면 된다.
- 리스트에 이미 데이터가 있을 경우
리스트에 이미 데이터가 있다면 리스트의 가장 마지막에 데이터를 추가해준다. 노드의 포인트(next)를 타고 넘어가다 next == null이게 되면 리스트의 마지막임을 알 수 있다.
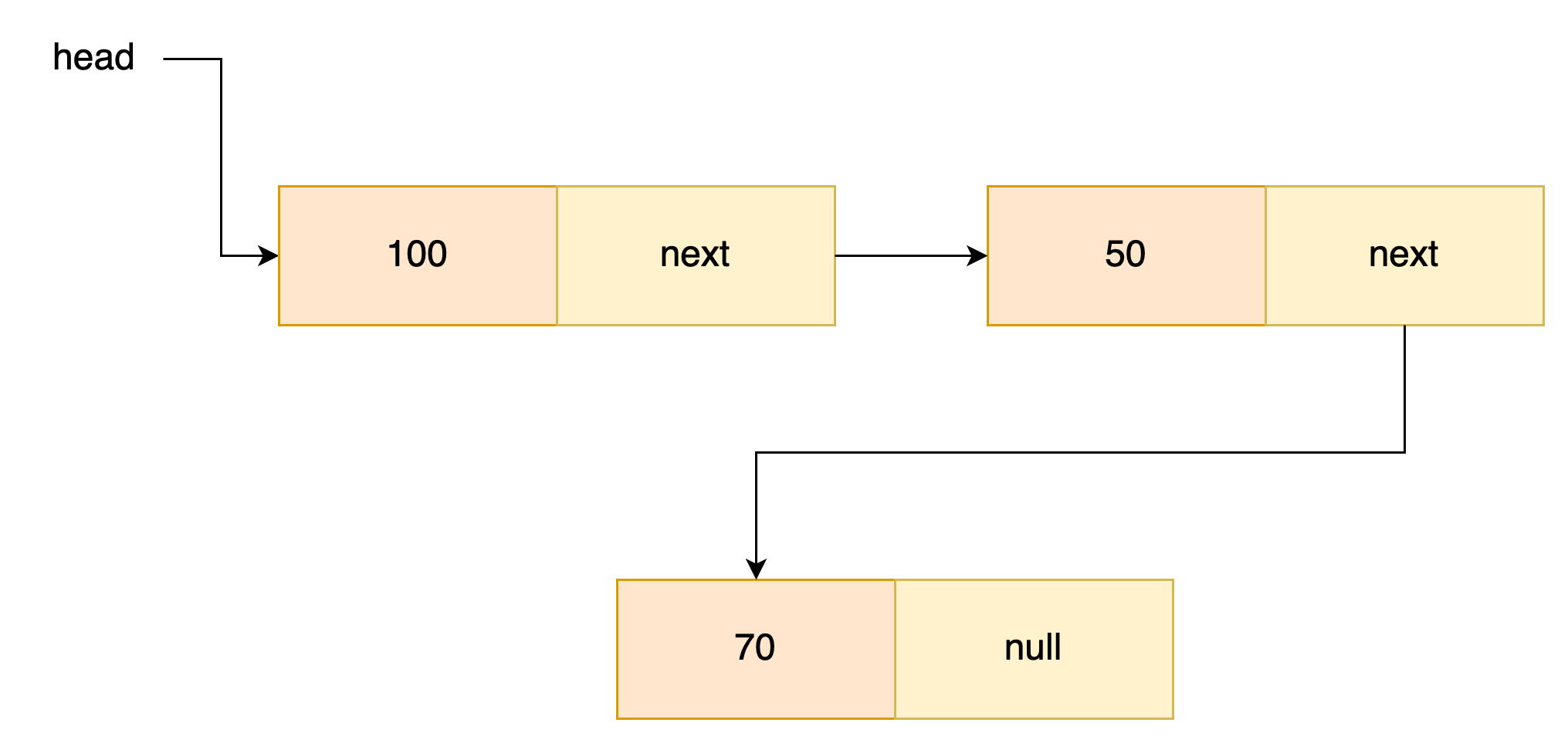
해당 내용에대한 코드는 아래와 같다.
public class SingleLinkedList <T>{
public Node<T> head = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
//데이터 추가
public void addNode(T data){
if (head == null){
//헤드가 없으면 첫시작이라는뜻
head = new Node(data);
}else {
//헤드로부터 시작해 링크드 리스트의 끝에 도달하면 그 마지막에 노드를 추가한다.
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node.next != null){
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new Node<>(data);
}
}
public void printAll(){
if (head != null){
Node<T> node = this.head;
System.out.println(node.data);
while (node.next != null){
node = node.next;
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList<Integer> singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList<Integer>();
singleLinkedList.addNode(100);
singleLinkedList.addNode(50);
singleLinkedList.addNode(70);
singleLinkedList.printAll();
/*100
50
70*/
}
노드 검색
사용자가 입력한 데이터가 리스트에 존재하는 지 확인하는 검색 기능을 추가해본다.
헤드 시작해서 next == null이 될때까지 루프를 돌리며 데이터를 비교한다. 데이터를 찾으면 해당 노드를 리턴한다.
public class SingleLinkedList <T>{
public Node<T> head = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
public Node<T> search(T data){
if (head != null) {
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node != null) {
if (node.data == data) {
return node;
} else {
node = node.next;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
중간에 노드 추가
- 먼저 newNode를 생성한다.
- newNode의 next 포인터가 이전 노드의 next가 가리키는 노드를 가리키도록 한다.
- 이전 노드의 next 포인터가 newNode를 가리키도록 하면 된다.
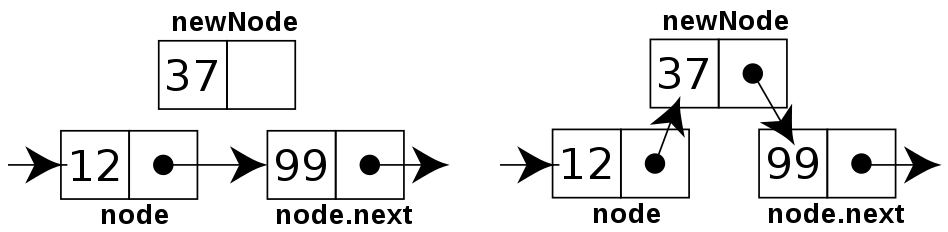
해당 내용에대한 코드는 아래와 같다.
public class SingleLinkedList <T>{
public Node<T> head = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
//데이터 추가
public void addNode(T data){
if (head == null){
//헤드가 없으면 첫시작이라는뜻
head = new Node(data);
}else {
//헤드로부터 시작해 링크드 리스트의 끝에 도달하면 그 마지막에 노드를 추가한다.
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node.next != null){
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new Node<>(data);
}
}
public Node<T> search(T data){
if (head != null) {
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node != null) {
if (node.data == data) {
return node;
} else {
node = node.next;
}
}
}
return null;
}
//데이터 중간 삽입
public void addNodeInside(T data, T isData){
Node<T> searchData = this.search(isData);
if (searchData == null){
this.addNode(data);
}else {
Node<T> nextNode = searchData.next;
searchData.next = new Node<>(data);
searchData.next.next = nextNode;
}
}
public void printAll(){
if (head != null){
Node<T> node = this.head;
System.out.println(node.data);
while (node.next != null){
node = node.next;
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList<Integer> singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList<Integer>();
singleLinkedList.addNode(100);
singleLinkedList.addNode(50);
singleLinkedList.addNode(70);
singleLinkedList.addNodeInside(60, 50);
singleLinkedList.printAll();
/*100
50
60
70*/
}
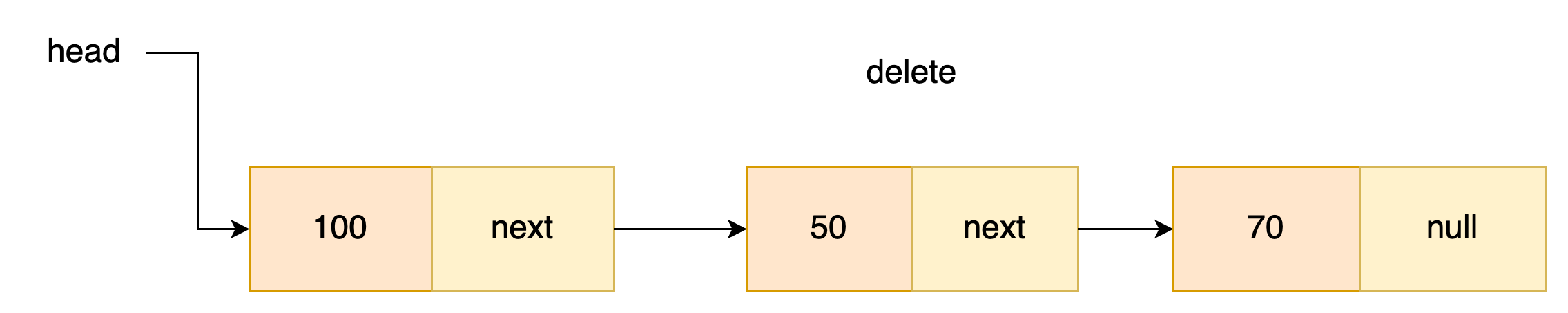
노드 삭제
노드 삭제는 노드 추가와 마찬가지로 두가지 경우가 있다.
- 헤드 노드 삭제
해드가 해드노드의 next를 가리키게 한다. 해드 노드는 가비지 컬렉터에의해 처리된다.
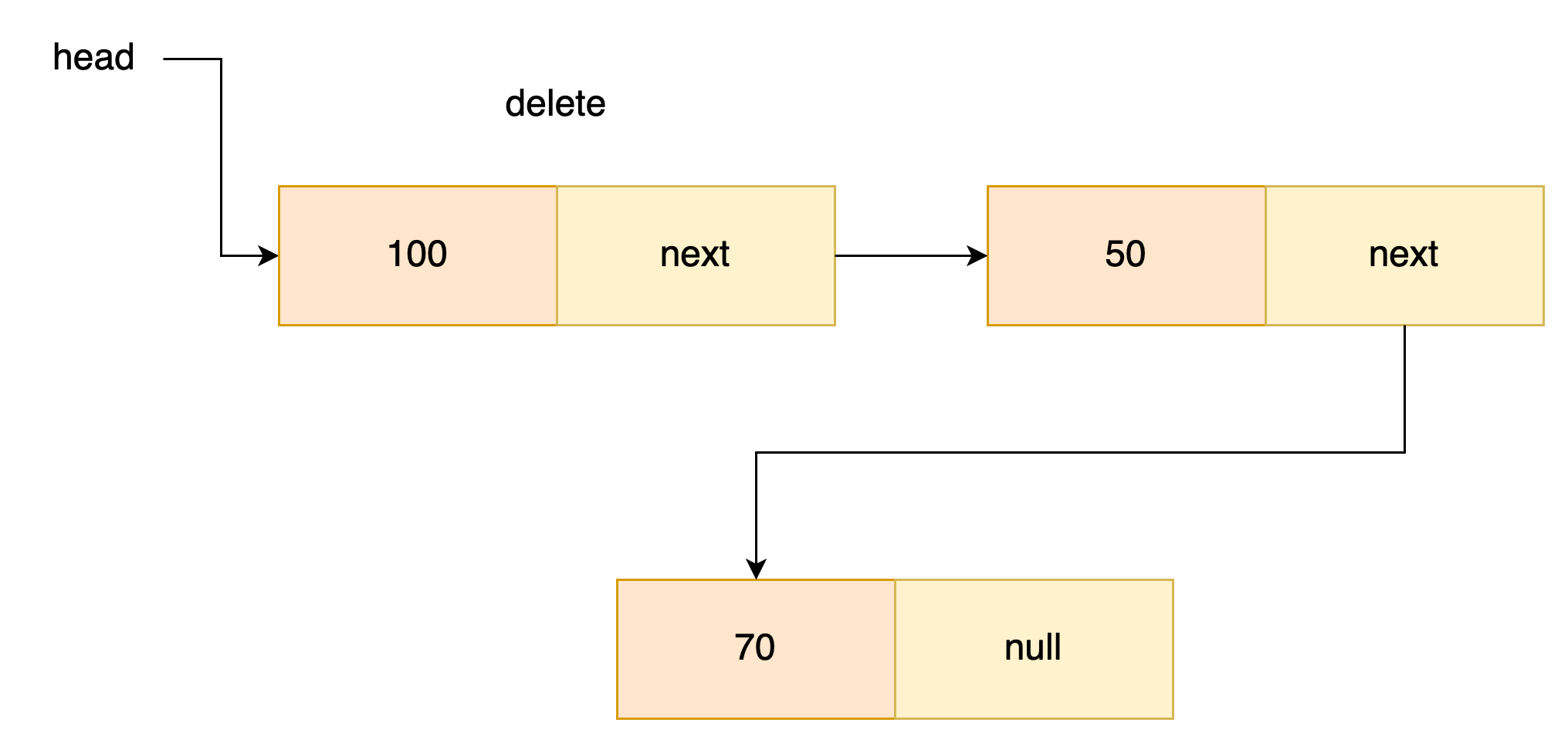
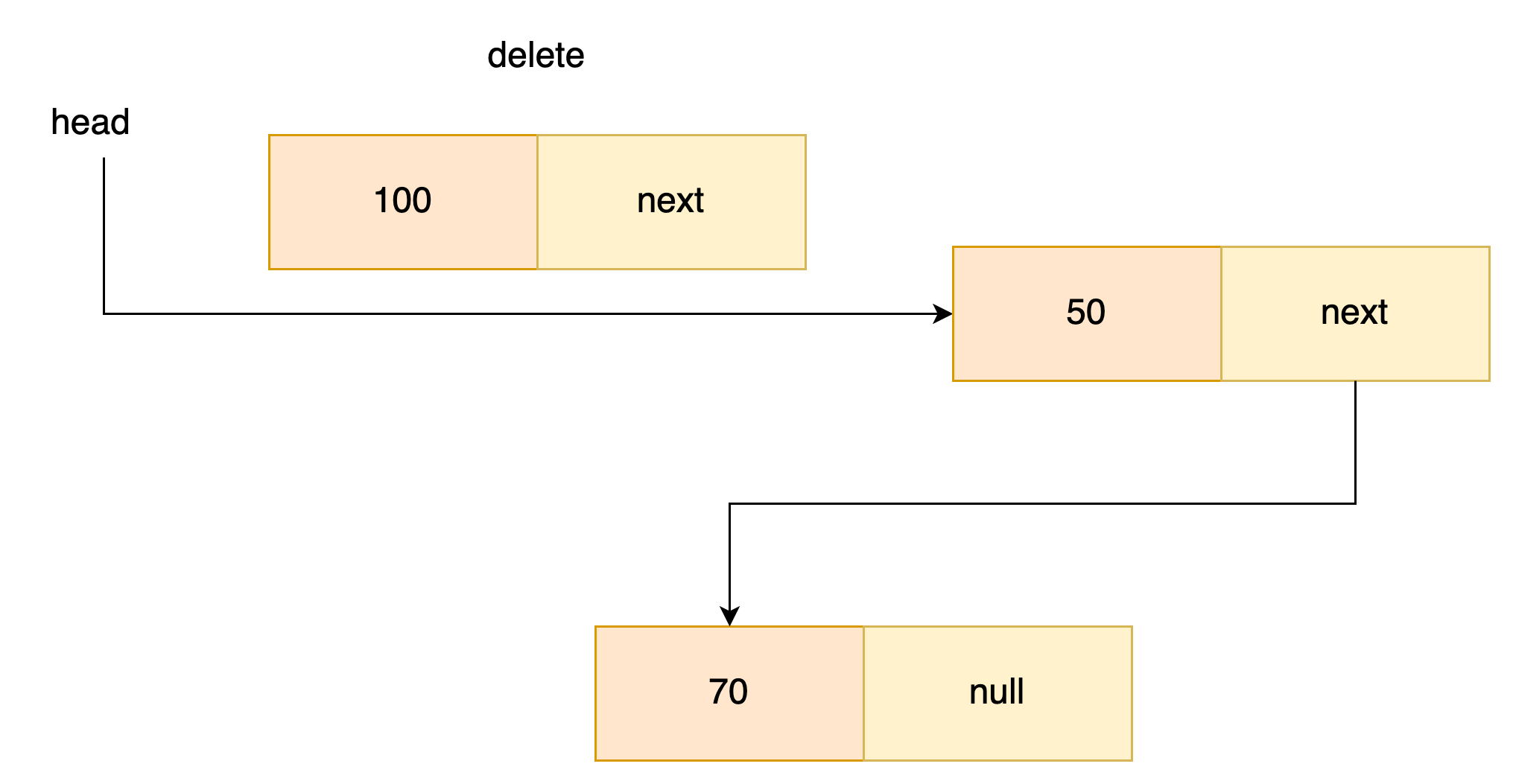
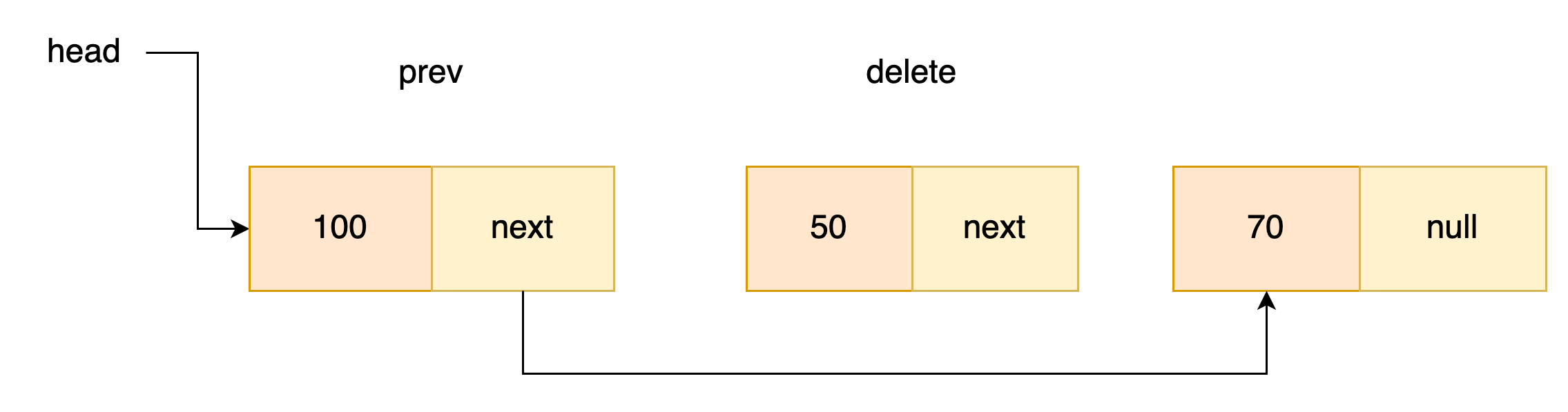
- 헤드 제외 노드 삭제
삭제할 노드의 이전 노드를 이용해야한다. prev.next가 제거할 노드를 찾았다면
prev.next가 prev.next.next를 가리키면 제거할 노드를 건너뛸 수 있다.
public class SingleLinkedList <T>{
public Node<T> head = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
public boolean delNode(T isData){
if (head == null){
return false;
}else {
Node<T> node = this.head;
if (node.data == isData){
this.head = this.head.next;
return true;
}else {
while (node.next != null){
if (node.next.data == isData){
node.next = node.next.next;
return true;
}
node = node.next;
}
return false;
}
}
}
public void printAll(){
if (head != null){
Node<T> node = this.head;
System.out.println(node.data);
while (node.next != null){
node = node.next;
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SingleLinkedList<Integer> singleLinkedList = new SingleLinkedList<Integer>();
singleLinkedList.addNode(100);
singleLinkedList.addNode(50);
singleLinkedList.addNode(70);
singleLinkedList.delNode(70);
singleLinkedList.printAll();
/*100
50
60*/
}
더블 링크드 리스트
각 노드가 선행 노드와 후속 노드에 대한 링크를 가지는 리스트이다.

노드 추가
노드 추가는 리스트가 비어있을때와 비저 있지 않았을때, 두가지로 나눌 수 있다.
- 리스트가 비어있을때
싱글 리스트와 비슷하다. 처음 노드를 추가할때는 그노드가 헤드이면서 테일이다. head, tail변수에 데이터를 넣어준다.
- 리스트가 있을때
싱글과 마찬가지로 반복문을돌려 리스트의 마지막으로 간다.
마지막 노드의 next에 추가할 노드를 연결해준다. 그리고 추가된 노드의 prev포인터를 마지막 노드와 연결해준다.
public class DoubleLinkedList<T> {
public Node<T> head = null;
public Node<T> tail = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> prev = null;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
public void addNode(T data){
if (this.head == null){
this.head = new Node<>(data);
this.tail = this.head;
}else {
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node.next != null){
node = node.next;
}
node.next = new Node<>(data);
node.next.prev = node;
this.tail = node.next;
}
}
public void printAll(){
if (this.head != null){
Node<T> node = this.head;
System.out.println(node.data);
while (node.next != null){
node = node.next;
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
}
}
노드 검색
더블 링크드 리스트는 앞뒤로 연결되어있어 앞에서부터 뿐만 아니라 뒤에서 부터도 검색이 가능하다.
정방향 검색은 싱글 링크드 리스트검색 방법과 같다. head로 부터 시작해 next 포인터로 뒤로 찾아간다.
역방향 검색은 정방향과 반대로하면된다. tail로 부터 시작해 prev 포인터로 앞으로 찾아간다.
public class DoubleLinkedList<T> {
public Node<T> head = null;
public Node<T> tail = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> prev = null;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
public Node<T> searchFromHead(T data){
if (head != null){
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node != null){
if (node.data == data){
return node;
}else {
node = node.next;
}
}
}
return null;
}
public Node<T> searchFromTail(T data){
if (this.tail != null){
Node<T> node = this.tail;
while (node != null){
if (node.data == data){
return node;
}else {
node = node.prev;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
중간에 노드 추가
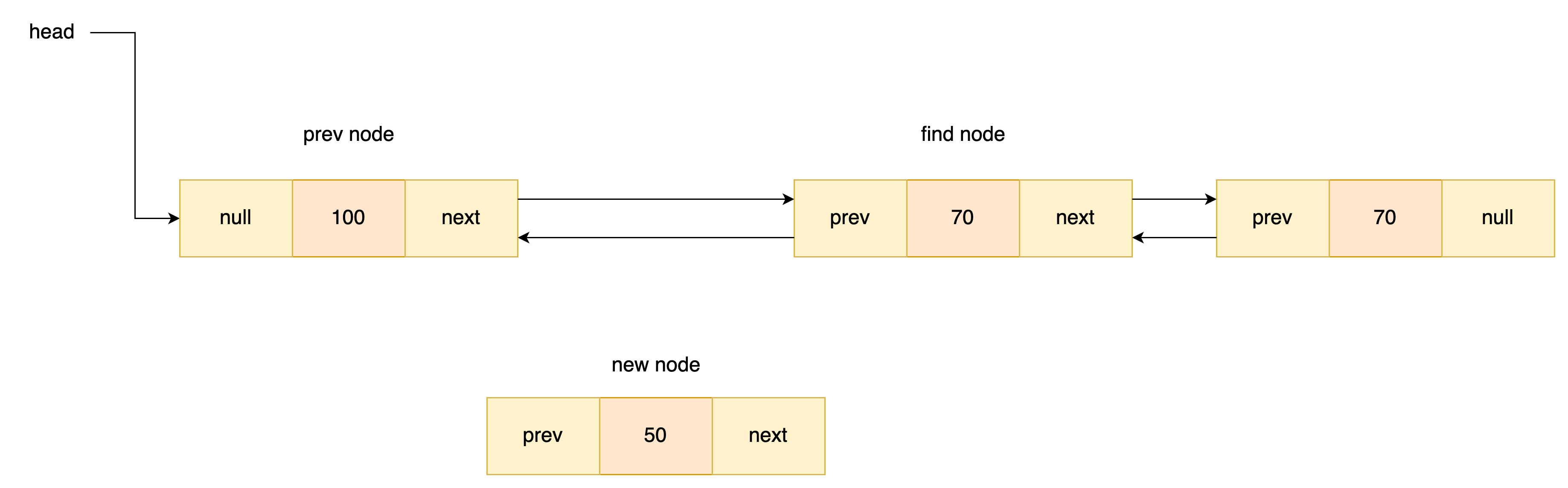
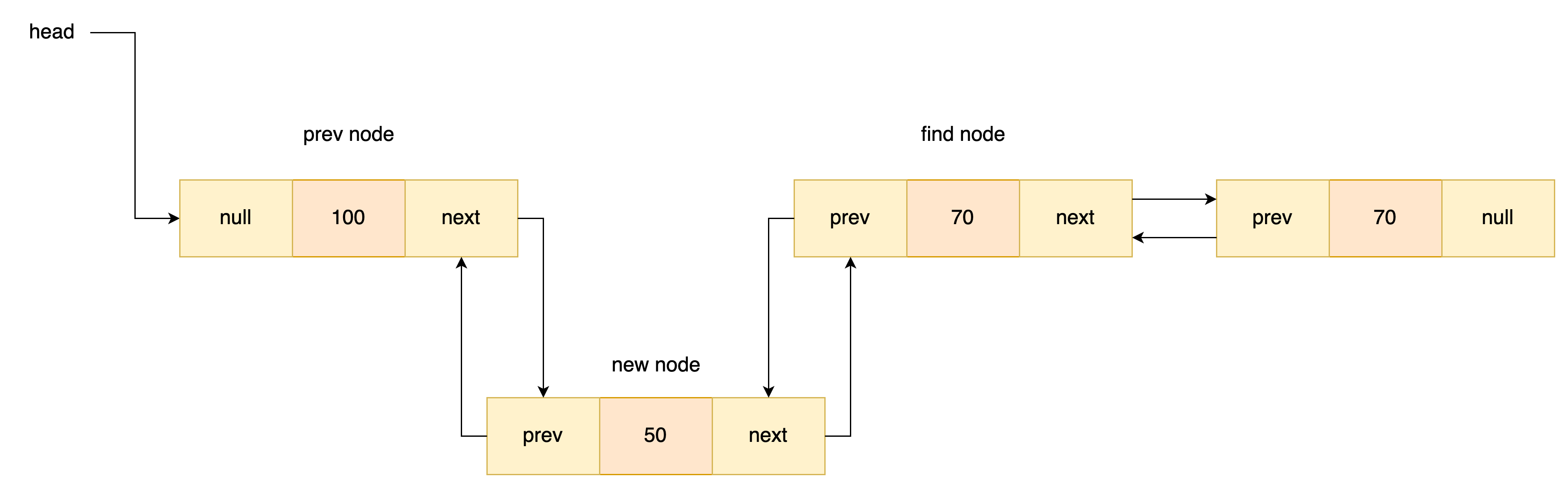
싱글 링크드와 방법은 같다. 다만 뒤로도 연결지 해줘야하기때문에 해당 부분을 추가 해주어야한다.
public class DoubleLinkedList<T> {
public Node<T> head = null;
public Node<T> tail = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> prev = null;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
public boolean addNodeToFront(T data, T nextData){
if (this.head == null){
this.head = new Node<T>(data);
this.tail = this.head;
return true;
}else if (this.head.data == nextData){
Node<T> newHead = new Node<>(data);
newHead.next = this.head;
this.head = newHead;
this.head.next.prev = this.head;
return true;
}else {
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node != null){
if (node.data == nextData){
Node<T> nodePrev = node.prev; //찾은 노드의 앞 노드
//정방향 연결
nodePrev.next = new Node<>(data); //찾은 노드의 앞에있는 노드 뒤에, 새로 노드를 만들어 연결한다.
nodePrev.next.next = node; //새로 만든 노드 뒤에 찾은 노드를 연결한다.
//역방향 연결
nodePrev.next.prev = nodePrev; //새로 생성된 노드의 앞에, 찾은 노드 앞에있는 노드를 연결한다.
node.prev = nodePrev.next; //새로 생성된 노드를 찾은 노드 앞에 연결한다.
return true;
}else {
node = node.next;
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
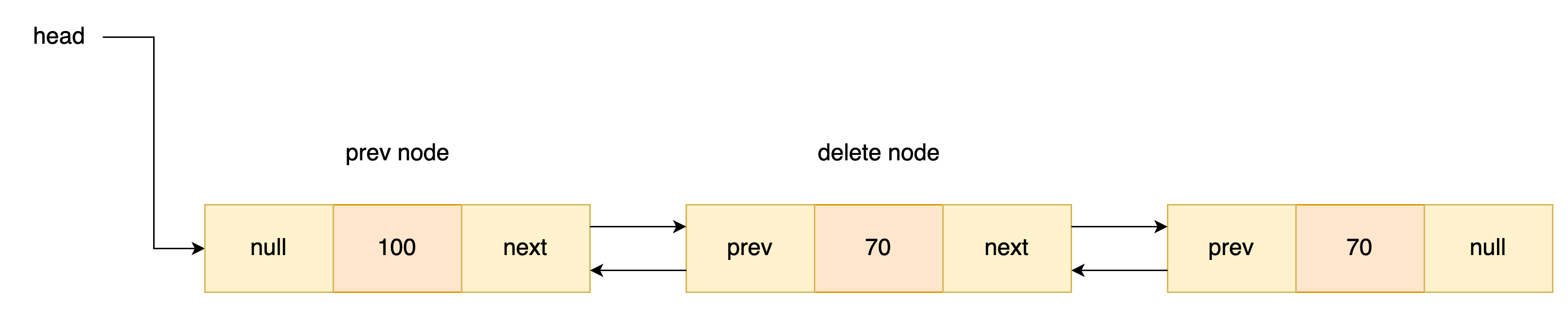
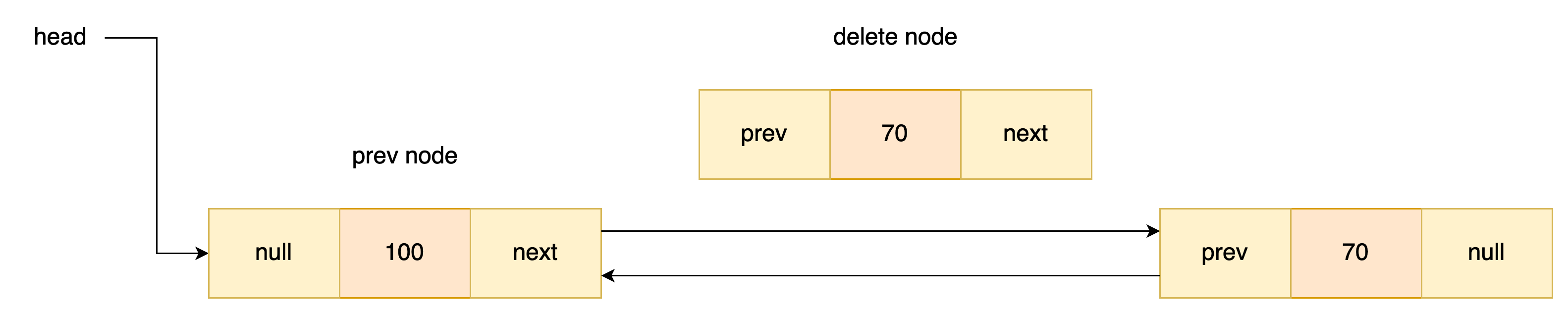
노드 삭제
삭제도 싱글 리스트와 비슷하다 먼저 헤드일때 테일일때를 확인하고 head일때는 prev, tail일때는 next의 포인트를 없앤다.
그리고 나머지의 경우는 삭제할 노드의 앞 뒤에있는 노드을 양쪽으로 연결시켜주면 된다.
public class DoubleLinkedList<T> {
public Node<T> head = null;
public Node<T> tail = null;
public class Node<T>{
T data;
Node<T> prev = null;
Node<T> next = null;
public Node(T data){
this.data = data;
}
}
public boolean delNode(T data){
if (head == null){
return false;
}else if (this.head.data == data){
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
return true;
}else if (this.tail.data == data){
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
return true;
}else {
Node<T> node = this.head;
while (node != null){
if (node.data == data){
Node<T> nodePrev = node.prev; //찾은 노드의 앞노드
nodePrev.next = node.next; //삭제할 노드의 앞부분 분리 후 연결
node.next.prev = nodePrev; //삭제할 노드의 뒷부분 분리 후 연결
return true;
}else {
node = node.next;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
