[Algorithm] 8장 자료구조 - 힙(Heap)

힙(Heap)
데이터에서 최대값과 최소값을 빠르게 찾기 위해 고안된 완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree) 자료구조이다.
- 완전 이진 트리 - 노드를 삽입할 때 최하단 왼쪽 노드부터 차례대로 삽입하는 트리
시간 복잡도
배열에 데이터를 넣고, 최대값과 최소값을 찾으려면 O(n) 이 걸린다. 이에 반해, 힙에 데이터를 넣고, 최대값과 최소값을 찾으면, O(log n)이 걸린다.
우선순위 큐와 같이 최대값 또는 최소값을 빠르게 찾아야 하는 자료구조 및 알고리즘 구현 등에 활용된다.
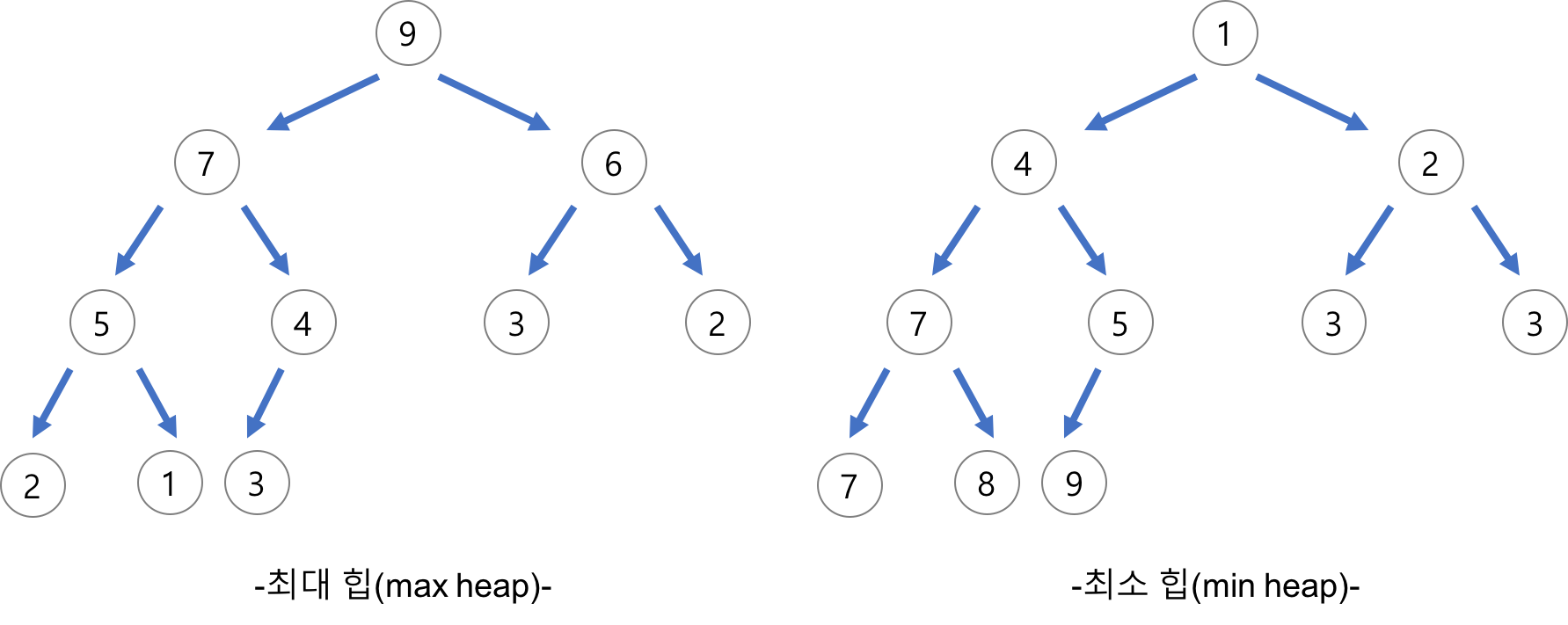
힙의 종류
- 최대 힙
- 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 크거나 같은 완전 이진 트리
- • key(부모 노드) >= key(자식 노드)
- 최소 힙
- 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 작거나 같은 완전 이진 트리
- key(부모 노드) <= key(자식 노드)
힙 동작
삽입과 삭제 기본동작을을 확인해본다.
데이터 삽입 - 기본
힙은 완전 이진 트리이므로, 삽입할 노드는 기본적으로 왼쪽 최하단부 노드부터 채워지는 형태로 동작한다.
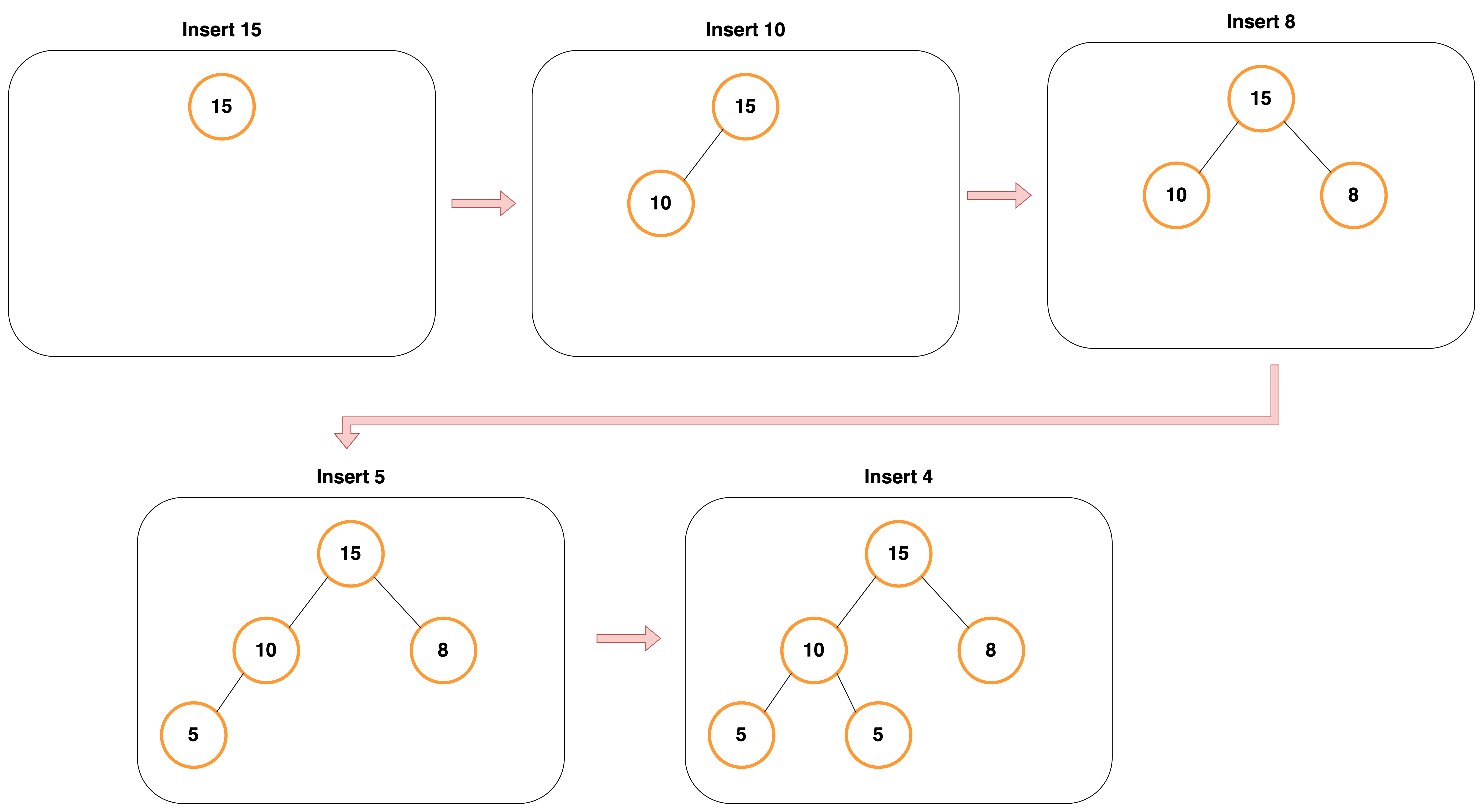
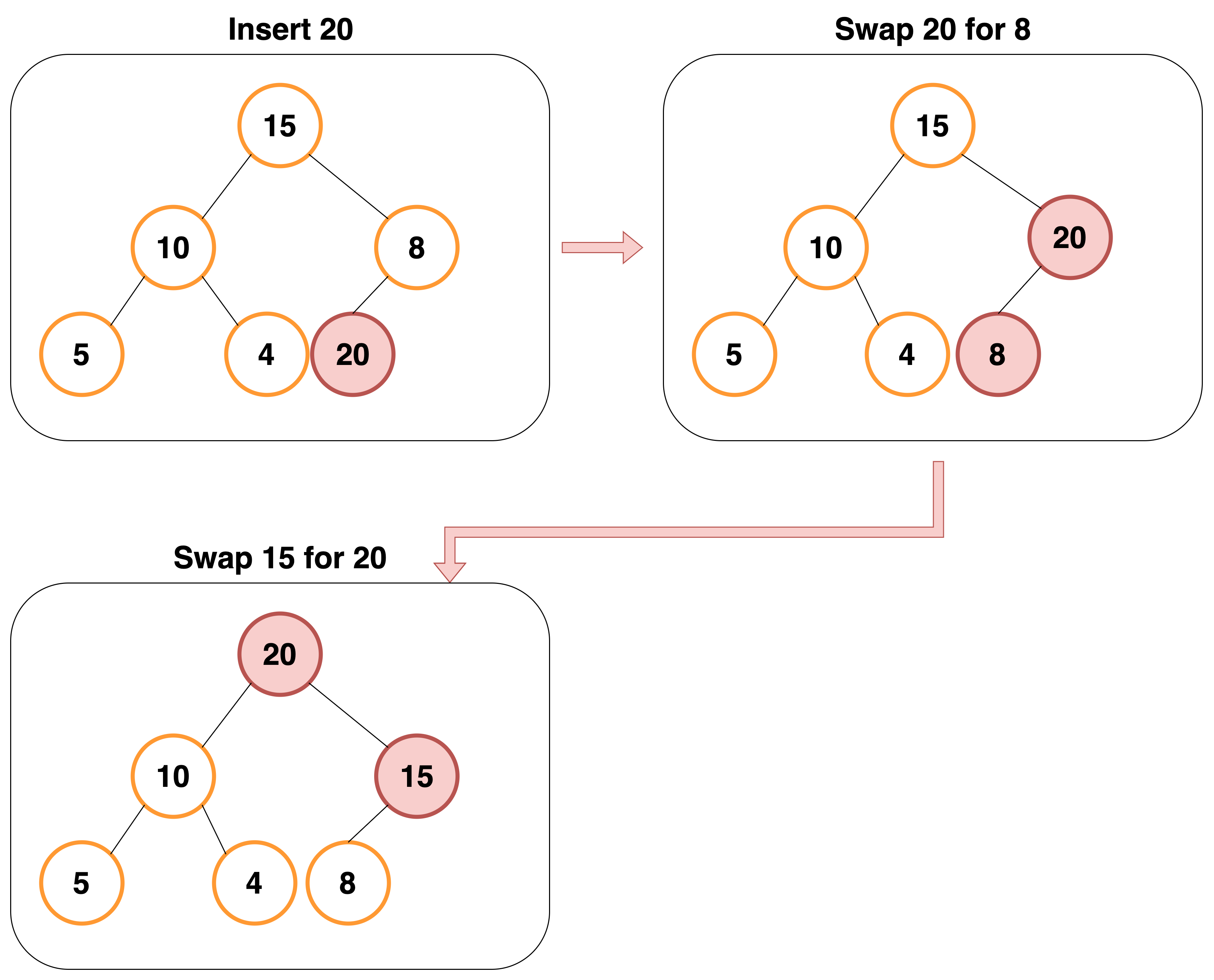
데이터 삽입 - 삽입할 데이터가 힙의 데이터보다 클 경우(max heap)
먼저 삽입된 데이터는 완전 이진 트리 구조에 맞추어, 최하단 왼쪽 노드부터 채워진다.
채워진 노드 위치에서, 부모 노드보다 값이 클 경우, 부모 노드와 위치를 바꾸는 작업을 반복한다.
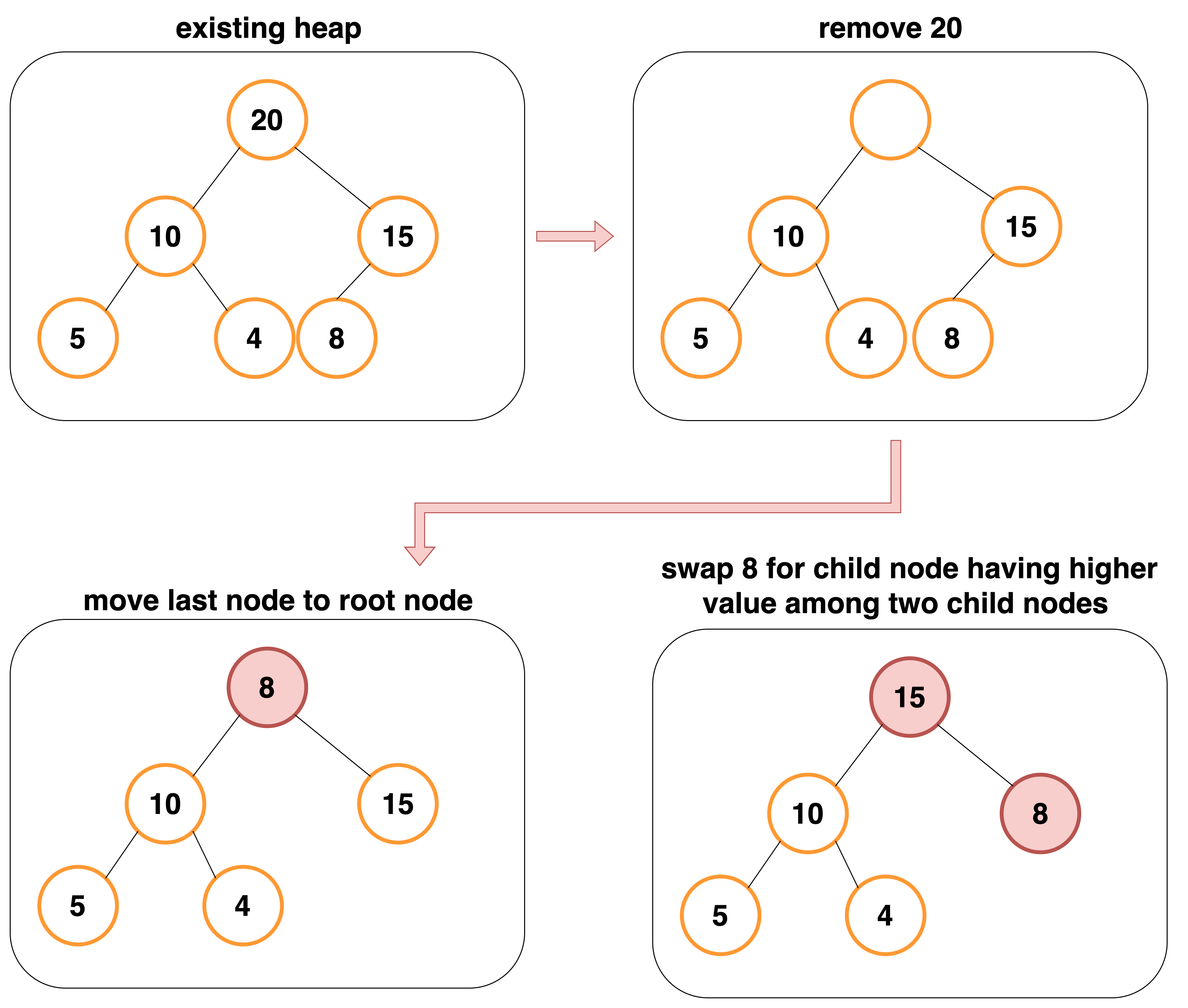
데이터 삭제(max heap)
힙의 용도는 최대값 또는 최소값을 root에 놓아서 값을 바로 꺼내 쓸 수 있도록 하는것이기 때문에 최상단 노드(root 노드)를 삭제하는 것이 일반적이다.
데이터 삭제시 가장 최하단부 왼쪽에 위치한 노드(가장 마지막에 추가한 노드)를 root 노드로 이동한다.
root 노드의 값이 child 노드보다 작을 경우, root 노드의 child 노드중 가장 큰 값을 가진 노드와 root 노드의 위치를 바꿔주는 작업을 반복한다.
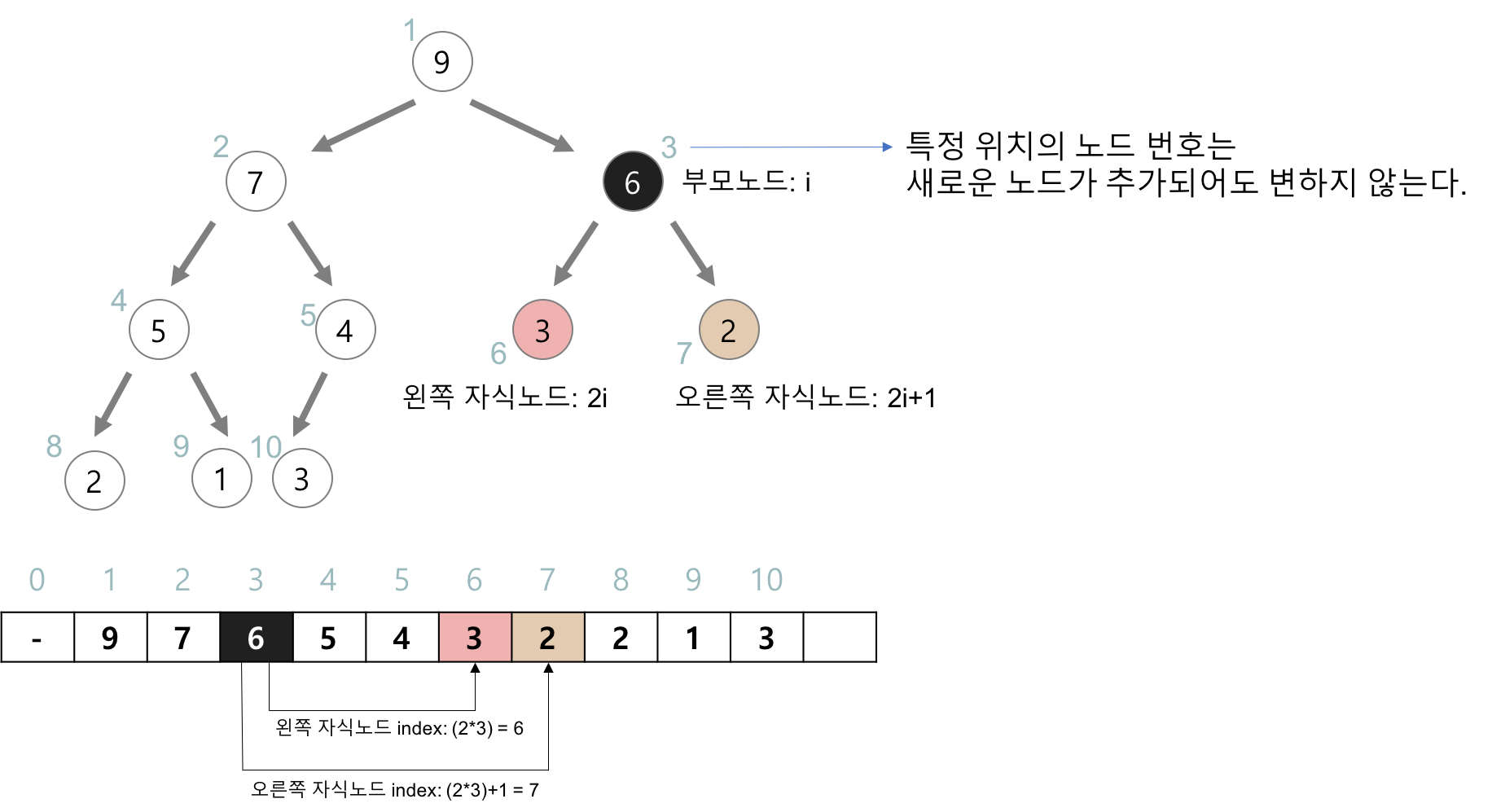
힙 구현
힙을 저장하는 표준적인 자료구조는 배열이다.
구현을 쉽게 하기 위해 배열의 첫 번째 인덱스인 0은 사용되지 않는다.
- 부모 노드 인덱스 = 자식 노드 인덱스 / 2
- 왼쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 = 부모 노드 인덱스 * 2
- 오른쪽 자식 노드 인덱스 = 부모 노드 인덱스 * 2 + 1
데이터 삽입 구현
먼저 어레이 리스트를 사용해 힙을 구현해 보자
public class MyHeap {
public ArrayList<Integer> heapArray = null;
public MyHeap(Integer data){
heapArray = new ArrayList<>();
heapArray.add(null);
heapArray.add(data);
}
}
0번 인덱스는 항상 비어준다.
데이터 입력은 위에서 말했다시피 다음과 같은 과정을 거친다.
- 삽입한 노드가 부모 노드의 값보다 클 경우, 부모 노드와 삽입한 노드 위치를 바꾼다.
- 삽입한 노드가 루트 노드가 되거나, 부모 노드보다 값이 작거나 같을 경우까지 반복한다.
해당 과정을 쉽게하기 위해 자바의 Collections.swap() 를 사용한다.
import java.util.Collections;
Collections.swap(List list, int a, int b)
- list - 스왑할 데이터들이 들어 있는 배열 변수
- a : 스왑할 데이터 인덱스 번호
- b : 스왑할 데이터 인덱스 번호
public class MyHeap {
public ArrayList<Integer> heapArray = null;
public MyHeap(Integer data){
heapArray = new ArrayList<>();
heapArray.add(null);
heapArray.add(data);
}
public boolean moveUp(Integer inserted_idx){
//인덱스가 1이면 하나밖에 없다는 뜻으로 노드를 교체할 필요가 없다.
if (inserted_idx <=1){
return false;
}
//해당 인덱스의 부모 인덱스
Integer parent_idx = inserted_idx/2;
//만약 부모 인덱스보다 현재 인덱스가 크다면 노드를 교체할 필요가 있으므로 참을 리턴한다.
return this.heapArray.get(inserted_idx) > this.heapArray.get(parent_idx);
}
public boolean insert(Integer data){
Integer inserted_idx, parent_idx;
//힙에 아무 데이터가 없을경우 리스트를 생성후 데이터를 넣어준다.
if (heapArray == null){
heapArray = new ArrayList<>();
heapArray.add(null);
heapArray.add(data);
return true;
}
//일단 리스트에 데이터를 추가해준다.
this.heapArray.add(data);
//추가된 데이터의 인덱스는 리스트의 마지막이다.
inserted_idx = this.heapArray.size()-1;
while (this.moveUp(inserted_idx)){
parent_idx = inserted_idx/2;
//부모 인덱스와 값을 교체한다.
Collections.swap(this.heapArray,inserted_idx,parent_idx);
//교체된 인덱스에서 다시 부모 인덱스와 비교한다.
inserted_idx = parent_idx;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHeap heapTest = new MyHeap(15);
heapTest.insert(10);
heapTest.insert(8);
heapTest.insert(5);
heapTest.insert(4);
heapTest.insert(20);
System.out.println(heapTest.heapArray);
}
}
데이터 삭제 구현
상단의 데이터 삭제시, 가장 최하단부 왼쪽에 위치한 노드 (일반적으로 가장 마지막에 추가한 노드) 를 root 노드로 이동한다.
root 노드의 값이 child node 보다 작을 경우, root 노드의 child node 중 가장 큰 값을 가진 노드와 root 노드 위치를 바꿔주는 작업을 반복한다.
public class MyHeap {
public ArrayList<Integer> heapArray = null;
public MyHeap(Integer data){
heapArray = new ArrayList<>();
heapArray.add(null);
heapArray.add(data);
}
public boolean moveDown(Integer popped_idx){
Integer left_child_popped_idx, right_child_popped_idx;
left_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2;
right_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2 + 1;
/* case1 왼쪽 자식도 없을때(모든 자식이 없을때) */
//만약 자식 인덱스가 리스트의 크기와 같거나 크다면 없다는 뜻이다.
if (left_child_popped_idx >= this.heapArray.size()){
return false;
/* case2 오른쪽 자식 노드만 없을때 */
}else if(right_child_popped_idx >= this.heapArray.size()){
//왼쪽 자식이 자기보다 크다면 서로 교체한다.
if (this.heapArray.get(popped_idx) < this.heapArray.get(left_child_popped_idx)){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
/* case3 왼쪽, 오른쪽 자식 노드가 모두 있을때 */
}else {
//자식들중 가장 큰 값을 자신과 비교한다.
if (this.heapArray.get(left_child_popped_idx) > this.heapArray.get(right_child_popped_idx)){
if (this.heapArray.get(popped_idx) < this.heapArray.get(left_child_popped_idx)){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}else {
if (this.heapArray.get(popped_idx) < this.heapArray.get(right_child_popped_idx)){
return true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
public Integer pop(){
Integer returned_data, popped_idx, left_child_popped_idx ,right_child_popped_idx;
if (this.heapArray.size() <= 1){
return null;
}
// 리턴할 값을 미리 빼둔다.
returned_data = this.heapArray.get(1);
//처음(가장 큰 값)인덱스와 마지막 인덱스의 값을 바꾼후 마지막 인덱스의 데이터를 삭제한다.
this.heapArray.set(1, this.heapArray.get(this.heapArray.size()-1));
this.heapArray.remove(this.heapArray.size()-1);
//위의 코드로 인해 마지막 인덱스의 값이 첫번째 인덱스로 올라오게된다. 그리고 그값을 비교한다.
popped_idx = 1;
while (this.moveDown(popped_idx)){
left_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2;
right_child_popped_idx = popped_idx * 2 + 1;
//만약 자식 인덱스가 리스트의 크기와 같거나 크다면 없다는 뜻이다.
//비교한 뒤 현재 인덱스보다 큰 값이 있다면 교체한다.
if (right_child_popped_idx >= this.heapArray.size()){
Collections.swap(this.heapArray,popped_idx,left_child_popped_idx);
popped_idx = left_child_popped_idx;
}else {
if (this.heapArray.get(left_child_popped_idx) > this.heapArray.get(right_child_popped_idx)){
if (this.heapArray.get(popped_idx) < this.heapArray.get(left_child_popped_idx)){
Collections.swap(this.heapArray,popped_idx,left_child_popped_idx);
}
}else {
if (this.heapArray.get(popped_idx) < this.heapArray.get(right_child_popped_idx)){
Collections.swap(this.heapArray,popped_idx,right_child_popped_idx);
}
}
}
}
//처음에 미리 빼두었던 루트 인덱스의 값을 리턴한다.
return returned_data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHeap heapTest = new MyHeap(15);
heapTest.insert(10);
heapTest.insert(8);
heapTest.insert(5);
heapTest.insert(4);
heapTest.insert(20);
System.out.println(heapTest.heapArray);
heapTest.pop();
System.out.println(heapTest.heapArray);
}
}
트리를 먼저 해보아서 좀더 익숙하게 구현할 수 있었다.
입력과 출력이 다음과 같이 보인다.
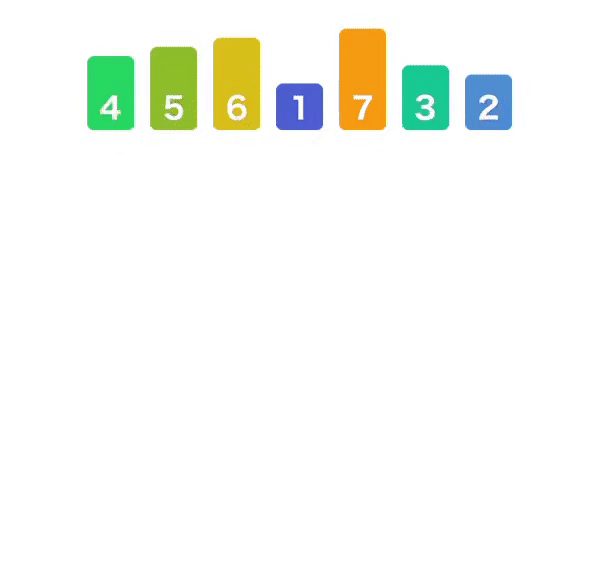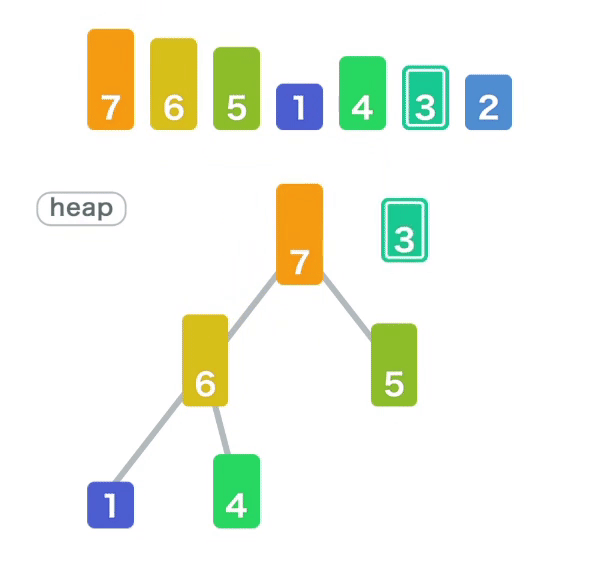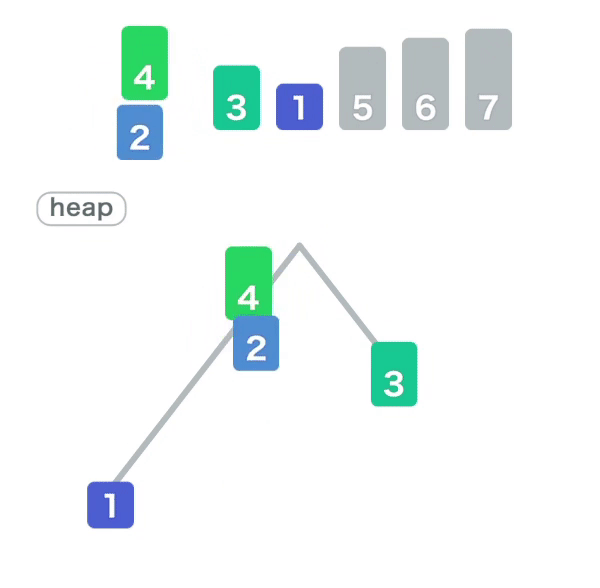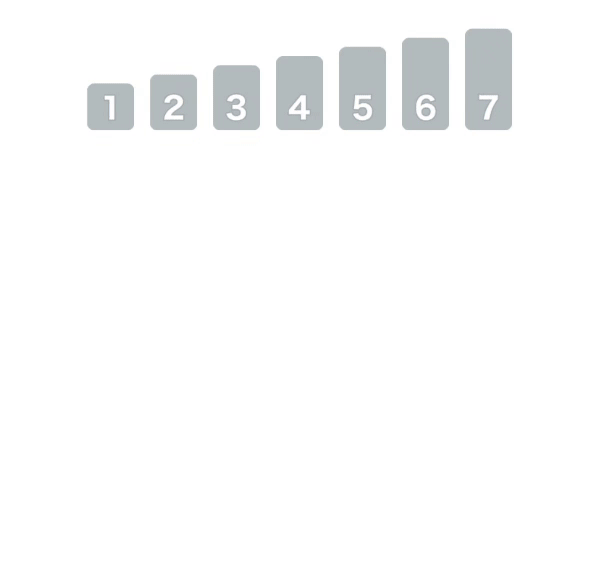
전체 코드는 여기서 확인하면 된다.
