[Algorithm] 3장 자료구조 - 큐 (Queue)

큐(Queue)
먼저 들어온 데이터가 먼저 나가는 구조이다. 즉, FIFO(First-In First-Out) 선입선출이다. 쉽게 생각해서 줄을 서는것과 같다.
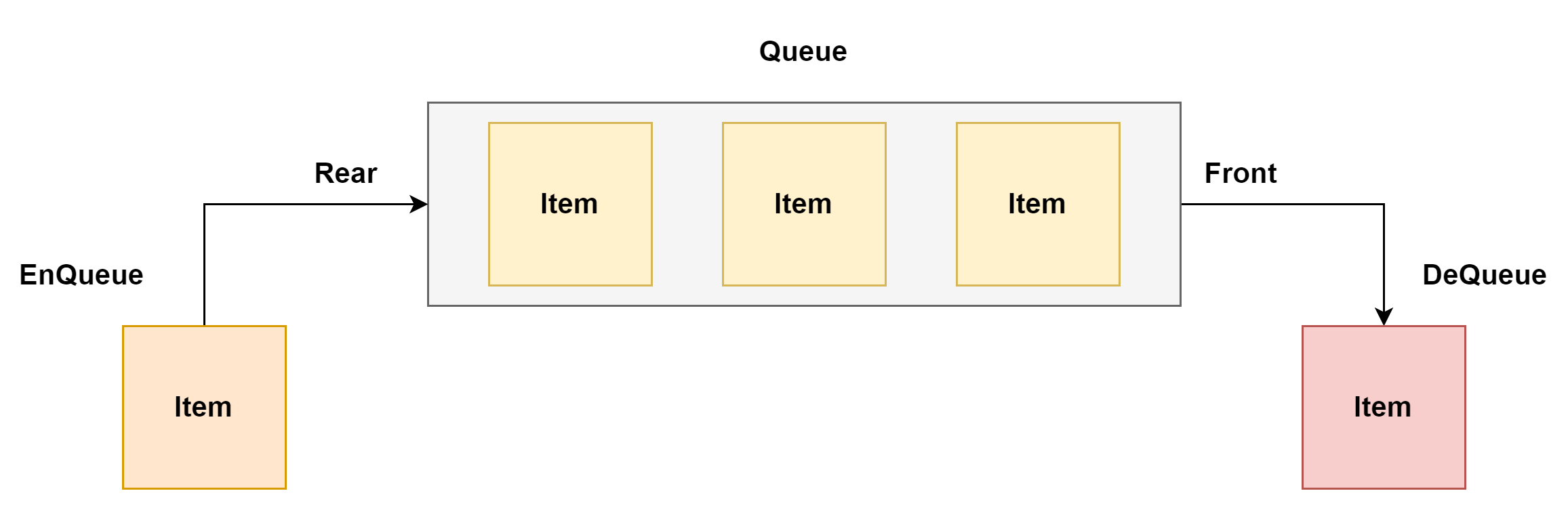
큐에서 삽입(Enqueue) 이 일어나는 곳을 Rear 라고 하며 삭제(Dequeue) 가 일어나는 곳을 Front 라고 한다.
자바에서 Queue 사용해보기
데이터 추가
Queue<Integer> queueInt = new LinkedList<Integer>(); // Integer 형 queue 선언
Queue<String> queueStr = new LinkedList<String>(); // String 형 queue 선언
// 데이터 추가는 add(value) 또는 offer(value) 를 사용한다.
queueInt.add(1);
queueStr.offer(2);
// Queue 인스턴스를 출력하면, 해당 큐에 들어 있는 아이템 리스트가 출력된다.
System.out.println(queueInt) //[1, 2]
데이터 삭제
// poll() 은 큐의 첫 번째 값 반환, 해당 값은 큐에서 삭제
queueInt.poll();
// poll() 과 마찬가지로, 첫 번째 값 반환하고, 해당 값은 큐에서 삭제
queueInt.remove()
사용 사례
데이터가 입력된 시간 순서대로 처리해야 할 필요가 있는 상황에 이용한다.
- 너비 우선 탐색(BFS, Breadth-First Search) 구현
- 처리해야 할 노드의 리스트를 저장하는 용도로 큐(Queue)를 사용한다.
- 노드를 하나 처리할 때마다 해당 노드와 인접한 노드들을 큐에 다시 저장한다.
- 노드를 접근한 순서대로 처리할 수 있다.
- 캐시(Cache) 구현
- 선입선출이 필요한 대기열 (티켓 카운터)
- 멀티 태스킹을 위한 프로세스 스케쥴링 방식을 구현하기 위해 많이 사용
큐 직접 만들어보기
큐를 자바에서 제공하는 클래스가아닌 직접 ArrayList를 사용하여 구현해보자.
public class MyQueue<T> {
private ArrayList<T> queue = new ArrayList<>();
public void enQueue(T item){
queue.add(item);
}
public T deQueue(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}else {
return queue.remove(0);
}
}
public Boolean isEmpty(){
return queue.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue<String> myQueue = new MyQueue<>();
myQueue.enQueue("Hello");
myQueue.enQueue("World");
System.out.println(myQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println(myQueue.deQueue());
System.out.println(myQueue.deQueue());
}
}
//결과
Hello
World
null
